1. Simple planar slicing¶
This example describes the planar slicing process for a simple shape, consisting out of a shape with a single contour (also known as a ‘vase’).
1.1. Imports and initialization¶
The first step is to import the required functions:
import time
import os
import logging
import compas_slicer.utilities as utils
from compas_slicer.pre_processing import move_mesh_to_point
from compas_slicer.slicers import PlanarSlicer
from compas_slicer.post_processing import generate_brim
from compas_slicer.post_processing import simplify_paths_rdp
from compas_slicer.post_processing import seams_smooth
from compas_slicer.print_organization import PlanarPrintOrganizer
from compas_slicer.print_organization import set_extruder_toggle
from compas_slicer.print_organization import add_safety_printpoints
from compas_slicer.print_organization import set_linear_velocity
from compas_slicer.print_organization import set_blend_radius
from compas_slicer.utilities import save_to_json
from compas_viewers.objectviewer import ObjectViewer
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
from compas.geometry import Point
Then we initiate logging to make sure that messages generated by compas_slicer are printed in the terminal.
logger = logging.getLogger('logger')
logging.basicConfig(format='%(levelname)s-%(message)s', level=logging.INFO)
Next we point to the data folder. Compas_slicer assumed there is a folder named data
where it looks for the model to slice. The model to slice can be of type .stl or .obj.
Also, we want to have a folder called output, where all of the output of our slicing
process can be stored. Therefore, we run the command get_output_directory(DATA), which
checks if the output folder exists and if not, it creates it.
DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data')
OUTPUT_DIR = utils.get_output_directory(DATA)
MODEL = 'simple_vase_open_low_res.obj'
1.2. Slicing process¶
In the next step we use the Compas function Mesh.from_obj to load our .obj
file. We then move it to the origin, but this can be any specified point, such as
a point on your printbed.
compas_mesh = Mesh.from_obj(os.path.join(DATA, MODEL))
move_mesh_to_point(compas_mesh, Point(0, 0, 0))
We then initialize the PlanarSlicer to initialize the slicing process.
The layer height needs to be specified by the user. Furthermore, the slicing_type
can be changed to use different methods of generating the ‘slices’. Currently,
three methods for slicing are supported:
default: Uses only standard compas functions, without external libraries, but can be a bit slow.cgal: Uses the ‘compas_cgal’ package, this is a very fast method but requires you to install compas_cgal.
The three methods will all return the slices of your model, so it is up to you to choose the method that you prefer.
slicer = PlanarSlicer(compas_mesh, slicer_type="cgal", layer_height=1.5)
slicer.slice_model()
After the model has been sliced, several post processing operations can be executed.
One useful functionality is generate_brim, which generates a number of layers
that are offset from the bottom layer, to improve adhesion to the build plate
(see image).
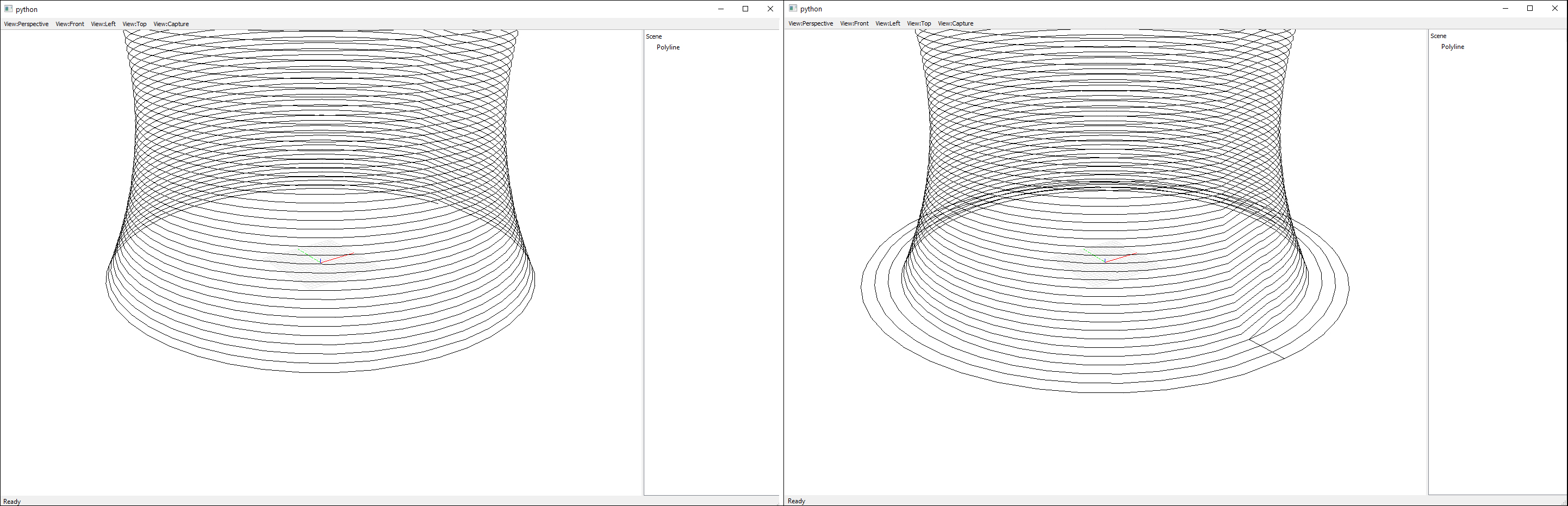
Left: Without brim. Right: With brim¶
generate_brim(slicer, layer_width=3.0, number_of_brim_offsets=4)
Depending on the amount of faces that your input mesh has, a very large amount of
points can be generated. simplify_paths_rdp is a function that removes points
that do not have a high impact on the final shape of the polyline. Increase the
threshold value to remove more points, decrease it to remove less. For more
information on how the algorithm works see: Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm
simplify_paths_rdp(slicer, threshold=0.6)
Currently the ‘seam’ between different layers of our shape is a ‘hard seam’,
the printer would move up almost vertically to move to the next layer.
To make the seam more ‘smooth’, and less visible we can use the
seams_smooth function.
seams_smooth(slicer, smooth_distance=10)
To get information on the current state of the slicing process we can print out information from the slicing process.
slicer.printout_info()
Since we are now done with operations involving the PlanarSlicer class,
we can save the slicing result to JSON. In the next steps we will use the
PlanarPrintOrganizer class to organize our print for fabrication.
save_to_json(slicer.to_data(), OUTPUT_DIR, 'slicer_data.json')
1.3. Print organization¶
In the next steps of the process we will use the PlanarPrintOrganizer to
make our slicing result ready for fabrication. First, we initialize the
PlanarPrintOrganizer and create PrintPoints. The difference between
PrintPoints and the compas.geometry.Points we were using in the
previous step is that the PrintPoints have additional functionality.
print_organizer = PlanarPrintOrganizer(slicer)
print_organizer.create_printpoints(compas_mesh)
We can add these additional functionalities to the printpoints by calling different functions.
set_extruder_toggle: Adds a boolean
extruder_toggleto the PrintPoints.Truemeans the extruder should be on (printing), whereasFalsemeans the extruder should be off (when traveling between paths).add_safety_printpoints: This function adds a ‘safety point’ (also known as ‘z-hop’) before and after print paths, to make sure the extruder does not collide with the print. This is recommended for prints consisting out of multiple contours.
set_linear_velocity: Sets the linear velocity (printing speed) for the print.
set_extruder_toggle(print_organizer, slicer)
add_safety_printpoints(print_organizer, z_hop=10.0)
set_linear_velocity(print_organizer, "constant", v=25.0)
After adding all of the fabrication-related parameters we an now first output the
Printpoints as data and then export them to a .JSON file.
printpoints_data = print_organizer.output_printpoints_dict()
save_to_json(printpoints_data, DATA, 'out_printpoints.json')
Finally, we can initialize the compas_viewer to visualize our results.
viewer = ObjectViewer()
print_organizer.visualize_on_viewer(viewer, visualize_polyline=True,
visualize_printpoints=False)
viewer.update()
viewer.show()
1.4. Final script¶
The completed final script can be found below:
import time
import os
import logging
import compas_slicer.utilities as utils
from compas_slicer.pre_processing import move_mesh_to_point
from compas_slicer.slicers import PlanarSlicer
from compas_slicer.post_processing import generate_brim
from compas_slicer.post_processing import simplify_paths_rdp
from compas_slicer.post_processing import seams_smooth
from compas_slicer.print_organization import PlanarPrintOrganizer
from compas_slicer.print_organization import set_extruder_toggle
from compas_slicer.print_organization import add_safety_printpoints
from compas_slicer.print_organization import set_linear_velocity
from compas_slicer.print_organization import set_blend_radius
from compas_slicer.utilities import save_to_json
from compas_viewers.objectviewer import ObjectViewer
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
from compas.geometry import Point
# ==============================================================================
# Logging
# ==============================================================================
logger = logging.getLogger('logger')
logging.basicConfig(format='%(levelname)s-%(message)s', level=logging.INFO)
# ==============================================================================
# Select location of data folder and specify model to slice
# ==============================================================================
DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data')
OUTPUT_DIR = utils.get_output_directory(DATA) # creates 'output' folder if it doesn't already exist
MODEL = 'simple_vase.obj'
start_time = time.time()
# ==========================================================================
# Load mesh
# ==========================================================================
compas_mesh = Mesh.from_obj(os.path.join(DATA, MODEL))
# ==========================================================================
# Move to origin
# ==========================================================================
move_mesh_to_point(compas_mesh, Point(0, 0, 0))
### --- Slicer
# options: 'default' : Both for open and closed paths. But slow
# 'cgal' : Very fast. Only for closed paths. Requires additional installation (compas_cgal).
slicer = PlanarSlicer(compas_mesh, slicer_type="cgal", layer_height=1.5)
slicer.slice_model()
# ==========================================================================
# Generate brim
# ==========================================================================
generate_brim(slicer, layer_width=3.0, number_of_brim_paths=3)
# ==========================================================================
# Simplify the paths by removing points with a certain threshold
# change the threshold value to remove more or less points
simplify_paths_rdp(slicer, threshold=0.3)
# ==========================================================================
# Smooth the seams between layers
# change the smooth_distance value to achieve smoother, or more abrupt seams
# ==========================================================================
seams_smooth(slicer, smooth_distance=10)
# ==========================================================================
# Prints out the info of the slicer
# ==========================================================================
slicer.printout_info()
# ==========================================================================
# Save slicer data to JSON
# ==========================================================================
save_to_json(slicer.to_data(), OUTPUT_DIR, 'slicer_data.json')
# ==========================================================================
# Initializes the PlanarPrintOrganizer and creates PrintPoints
# ==========================================================================
print_organizer = PlanarPrintOrganizer(slicer)
print_organizer.create_printpoints()
# ==========================================================================
# Set fabrication-related parameters
# ==========================================================================
set_extruder_toggle(print_organizer, slicer)
add_safety_printpoints(print_organizer, z_hop=10.0)
set_linear_velocity(print_organizer, "constant", v=25.0)
set_blend_radius(print_organizer, d_fillet=10)
# ==========================================================================
# Converts the PrintPoints to data and saves to JSON
# =========================================================================
printpoints_data = print_organizer.output_printpoints_dict()
utils.save_to_json(printpoints_data, OUTPUT_DIR, 'out_printpoints.json')
# ==========================================================================
# Initializes the compas_viewer and visualizes results
# ==========================================================================
viewer = ObjectViewer()
# slicer.visualize_on_viewer(viewer)
print_organizer.visualize_on_viewer(viewer, visualize_polyline=True,
visualize_printpoints=False)
viewer.view.use_shaders = False
viewer.update()
viewer.show()
end_time = time.time()
print("Total elapsed time", round(end_time - start_time, 2), "seconds")