Working in Grasshopper
To get COMPAS working in Grasshopper, you first have to install COMPAS for Rhino (see Working in Rhino). In Grasshopper, COMPAS is imported from within a GhPython component. Rhino for Mac and Rhino 6+ all come with their own GhPython interpreter, but if you use Rhino 5 on Windows, please download and install GhPython here.
Verify setup
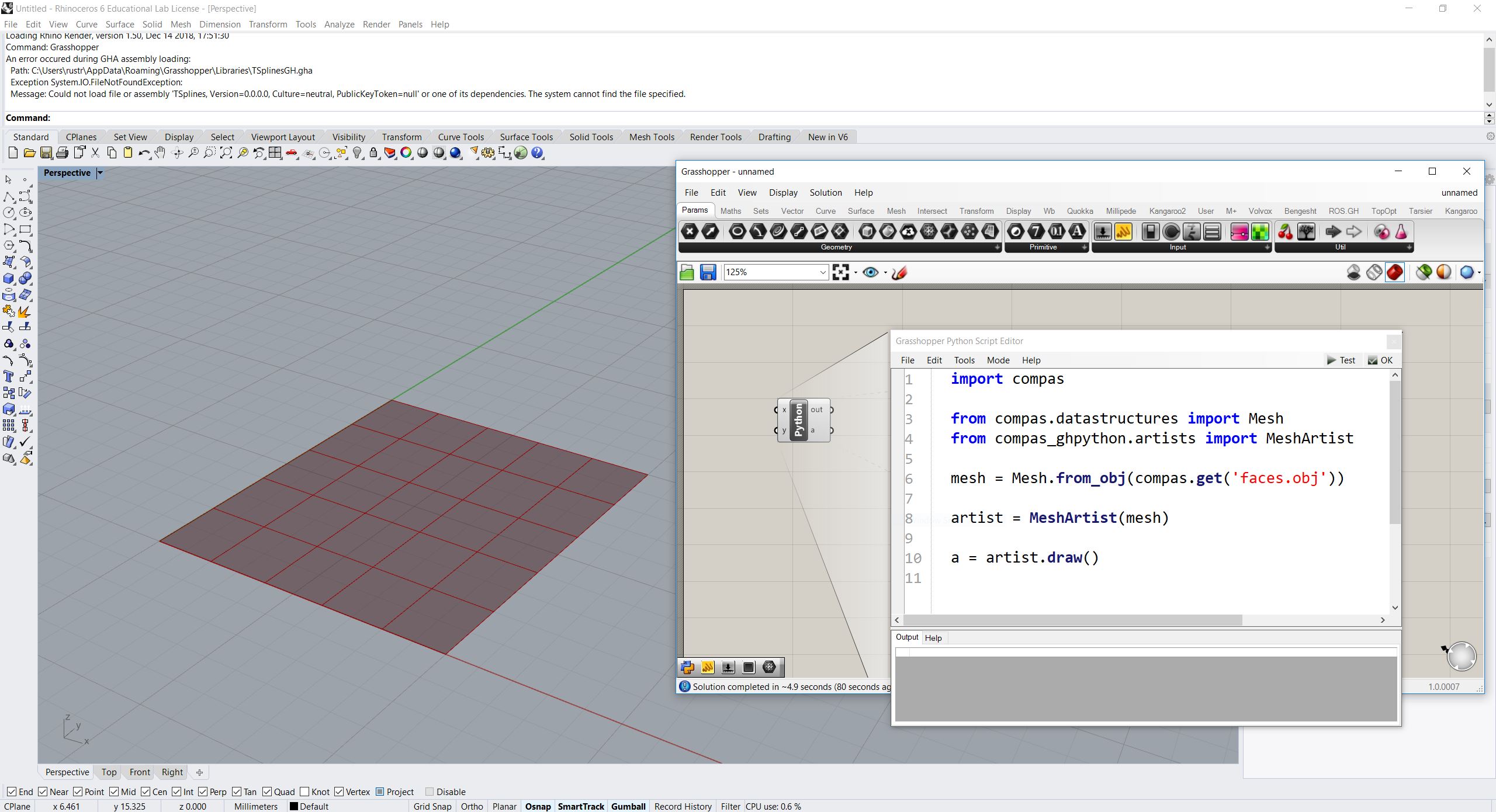
To verify that everything is working properly, simply create a GhPython component on your Grasshopper canvas, paste the following script and hit OK.
import compas
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
from compas.scene import Scene
mesh = Mesh.from_obj(compas.get('faces.obj'))
scene = Scene()
scene.add(mesh)
a = scene.draw()
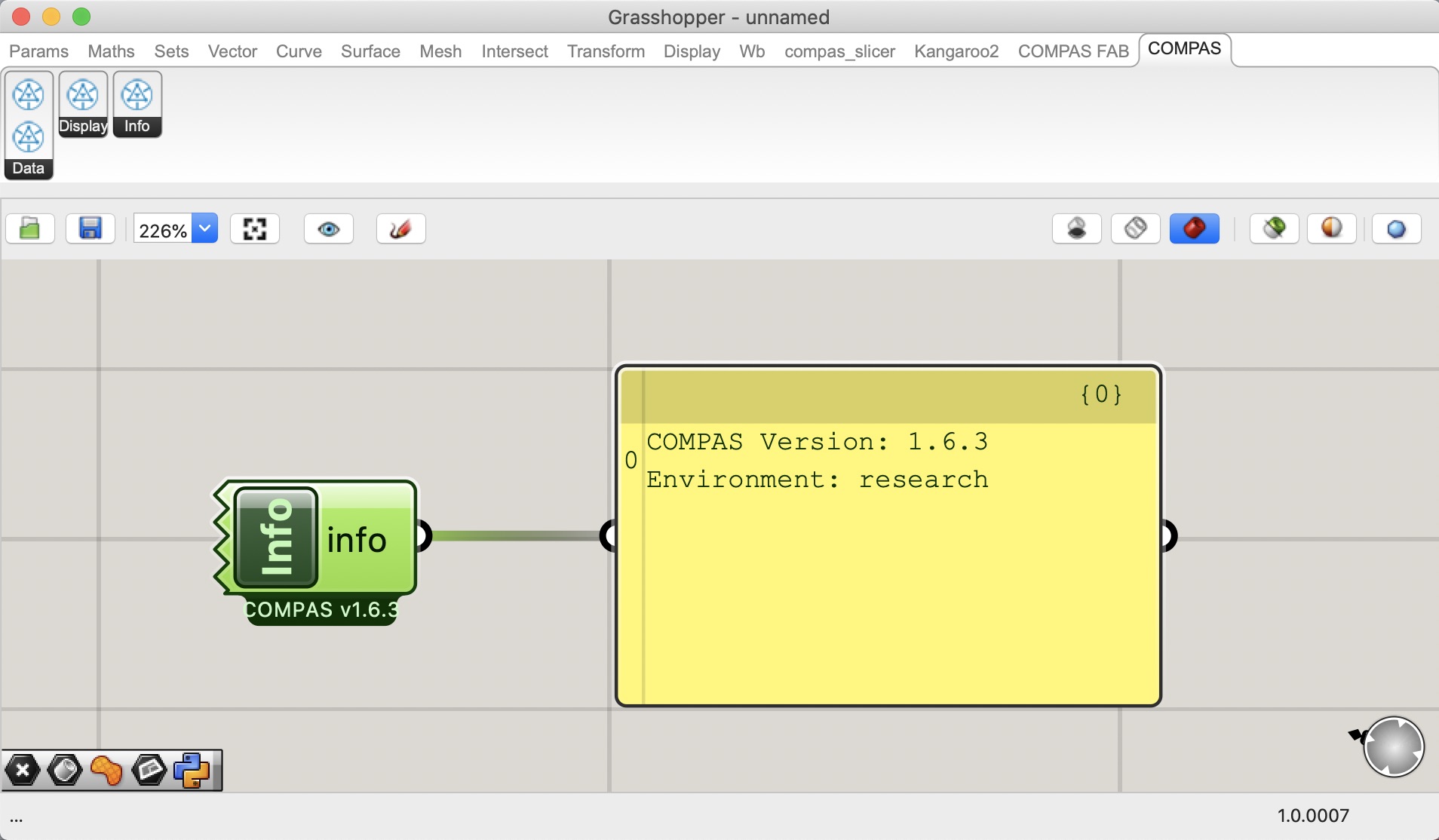
Grasshopper components for COMPAS
When COMPAS for Rhino is installed, it also installs Grasshopper components for COMPAS. For example, the current environment information can be retrieved with the INFO component.
Reloading changed libraries
If you change a Python library during a running Rhino application, which is
imported in a GhPython component (e.g. via import compas_fab),
it is necessary to reload the library so that the GhPython interpreter
recognizes the changes. To avoid restarting Rhino, you can use the method
unload_modules of DevTools. The following example reloads the library compas_fab.
from compas_rhino import DevTools
DevTools.unload_modules('compas_fab')
Note
Prefer using unload_modules as early as possible in your grasshopper workflow. Re-loading modules later might result, for example, in COMPAS not being able to find a SceneObject as well as other issues related to a mid-workflow re-definition of Python types.
Python Scripting Outside Rhino/Grasshopper with Auto-Reloading
Developing Python scripts outside of Rhino/Grasshopper allows you to take advantage of
modern code editors. However, this workflow requires two key steps: ensuring the Python
interpreter can access your script’s location and enabling automatic reloading of the
script when changes are made in your external editor.
If the scripts or modules you are working on are located in the same folder as the Rhino/Grasshopper file you are editing, the DevTools class can be used to make them importable and reload them automatically when modified.
This approach provides a seamless workflow for developing Python scripts in modern IDEs, such as Visual Studio Code, while running and testing the code inside Rhino/Grasshopper with minimal interruptions.
Enabling Auto-Reloading
To enable this feature, use the enable_reloader method of the DevTools class.
This makes all Python scripts in the same folder as the Grasshopper file importable
and ensures they automatically reload when changes are applied.
from compas_rhino import DevTools
DevTools.enable_reloader()
Note
Call this method early in your script to start the monitoring service immediately.
Importing Local Modules
Once auto-reloading is enabled, any script component that needs to use local modules can include the following at the top of the script:
from compas_rhino import DevTools
DevTools.ensure_path()
This ensures local modules are accessible. For instance, if a file named my_module.py is in
the same folder as your Grasshopper file, you can import it in a script component like this:
import my_module