Developing a GH Component
The COMPAS ecosystem offers excellent integration with Grasshopper. Thanks to the GHPython Componentizer it is possible to write Grasshopper components in Python, in a git friendly way, including the components’ code in the same repository as the rest of your project.
Note
To develop GH components using the GHPython Componentizer, you would need a development setup of COMPAS. See Development Setup for more information.
GHPython Componentizer
To use the Componentizer, it is recommended that your project’s repository be made from the cookiecutter template for COMPAS packages. This takes care of a lot of the boilerplate code, and makes compiling and installing the components so much easier.
The ghuser section in the tasks.py file of your project tell the Componentizer where to find the source code of your components, and where to put the generated components.
By default, the components’ code is expected in src/{your_package_name}/components folder of your project.
ns.configure(
{
"ghuser": {
"source_dir": "src/compas_bananas/components",
"target_dir": "src/compas_bananas/components/ghuser",
"prefix": "(COMPAS_BANANAS)",
},
}
)
Creating a component
Inside the source_dir folder, each component shall have its own folder with the following three files:
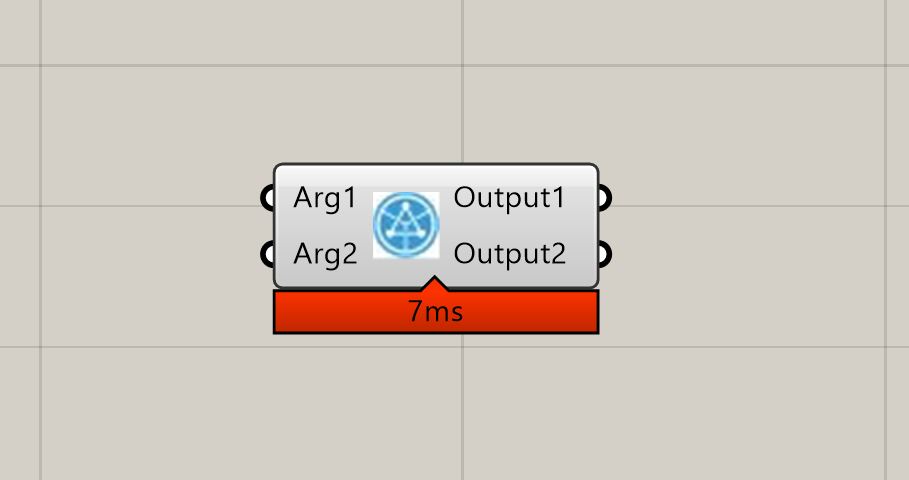
code.py- this is where our component’s code goesmetadata.json- this is where we let the Componentizer know about different settings of our componenticon.png- this icon will appear in GH. It must be exactly 24x24 pixels.
Note
By convension, we name the component folders with a two letter prefix, followed by an underscore, followed by the name of the component. For example, Cb_ExampleComponent.
src/compas_bananas/components/Cb_ExampleComponent
├── code.py
├── icon.png
└── metadata.json
Metadata
A typical metadata.json file has the following structure:
{
"name": "Example Component",
"nickname": "Example",
"category": "COMPAS Bananas",
"subcategory": "Example",
"description": "This is an example component.",
"exposure": 4,
"ghpython": {
"isAdvancedMode": true,
"iconDisplay": 0,
"inputParameters": [
{
"name": "Arg1",
"description": "First example argument.",
"typeHintID": "none",
"scriptParamAccess": 1
},
{
"name": "Arg2",
"description": "Second example argument.",
"typeHintID": "bool",
"scriptParamAccess": 0
}
],
"outputParameters": [
{
"name": "Output1",
"description": "First output."
},
{
"name": "Output2",
"description": "Second output."
}
]
}
}
For more information about the required fields and their possible values please visit GHPython Componentizer.
Code
The GHPython Componentizer only supports GHPython components in advanced mode.
This means each component must inherit from the ghpythonlib.component class and implement the RunScript() method.
A typical code file might look like this:
from ghpythonlib.componentbase import executingcomponent as component
class ExampleComponent(component):
def RunScript(self, Input1, Input2):
# do the work here
Output1 = None
Output2 = None
return Output1, Output2
Please not that the inputs to the RunScript() method must match the ones defined in the metadata.json file by name and number.
The outputs must also match the ones defined in the metadata.json file by name and number.
Icon
Finally, the component’s folder must include an icon used to represent the component in GH.
The icon must be a 24x24 pixel PNG file named icon.png.
Compiling the components
Note
IronPython 2.7 must be installed on your system in order to run the Componentizer. You can download it from here
In order to run the Componentizer make sure your dev virtual environment is activated and run
invoke build-ghuser-components
If everything went well, you should see at least the following output:
Processing component bundles:
[x] Cb_ExampleComponent => C:\Users\path_to_repo\src\project_slug\ghpython\components\ghuser\Cb_ExampleComponent.ghuser
If any error occurs, the Componentizer will let you know what went wrong.
Installing the components to Rhino
Once the components are compiled, and are in the target_dir folder, you can install them to Rhino by running
python -m compas_rhino.install -v 7.0
You should then see
Installing COMPAS packages to Rhino 7.0 scripts folder:
C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\McNeel\Rhinoceros\7.0\scripts
compas OK
compas_ghpython OK
compas_rhino OK
compas_bananas OK
Running post-installation steps...
compas_bananas OK: Installed 1 GH User Objects
You component should now appear in Grasshopper