Basics - Entity APIs
This tutorial shows how to use the Entity APIs to inspect and manipulate individual IFC entities.
We use a window element as an example.
>>> from compas_ifc.model import Model
>>> model = Model.from_ifc("data/Duplex_A_20110907.ifc")
>>> window = model.get_entities_by_type("IfcWindow")[0]
>>> window
<#6426 IfcWindow "M_Fixed:4835mm x 2420mm:4835mm x 2420mm:145788">
Visualization
Similar to the Model.show() function, you can use the Entity.show() function to visualize an individual entity.
>>> window.show()
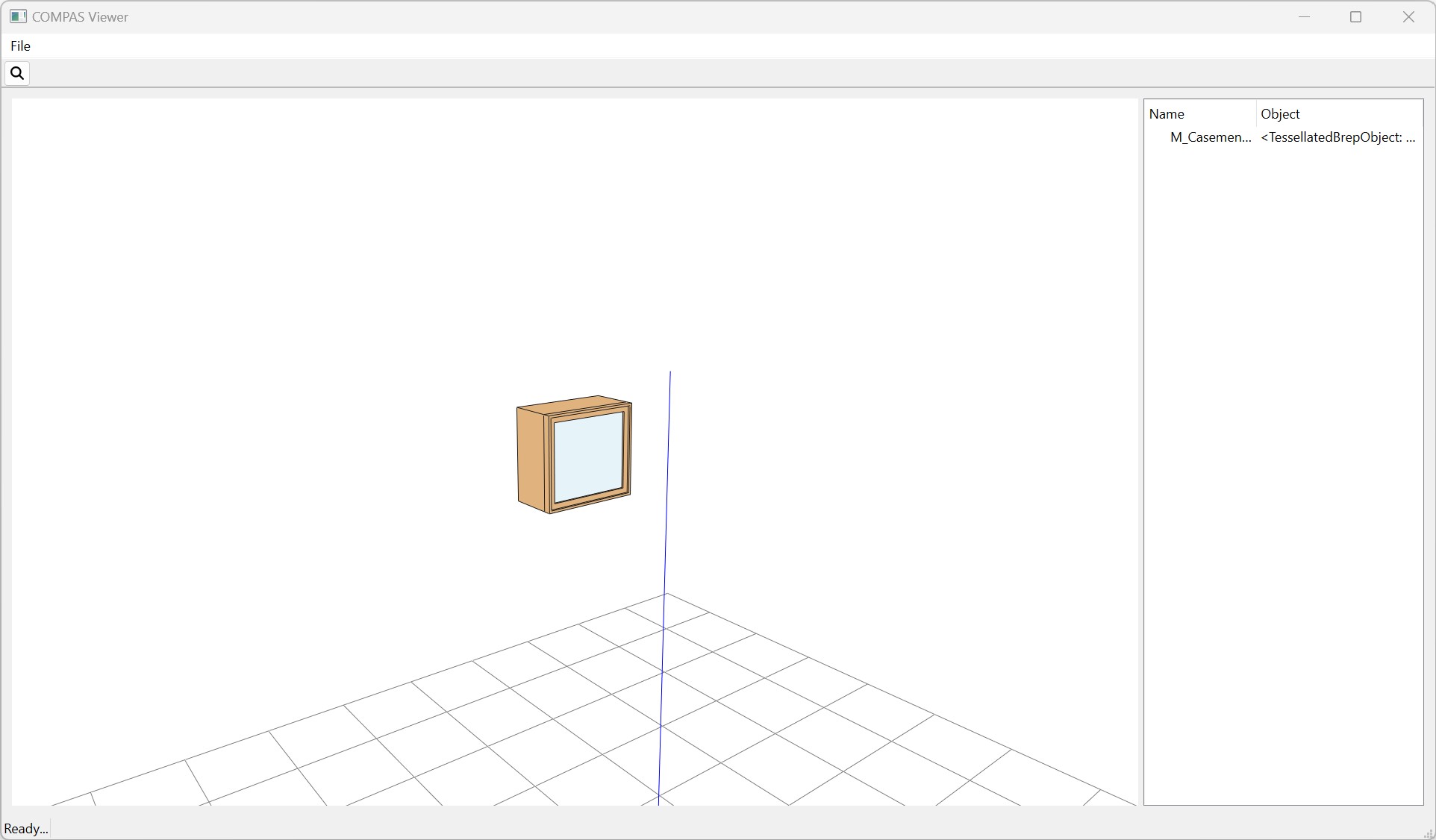
Entity Attributes
Each entity in an IFC model has a set of attributes regulated by the IFC standard,
such as general information like “Name”, “Description”, “Representation” and type specific information like “OverallHeight”, “OverallWidth” for classes like IfcWindow.
To access these attributes, you can use the attributes property.
>>> window.attributes
{'GlobalId': '1hOSvn6df7F8_7GcBWlR72', 'OwnerHistory': <#33 IfcOwnerHistory>, 'Name': 'M_Fixed:4835mm x 2420mm:4835mm x 2420mm:145788', 'Description': None, 'ObjectType': '4835mm x 2420mm', 'ObjectPlacement': <#6425 IfcLocalPlacement>, 'Representation': <#6420 IfcProductDefinitionShape>, 'Tag': '145788', 'OverallHeight': 2.419999999999998, 'OverallWidth': 4.834999999999996}
You can also directly access these attributes by calling them in CamelCase,
meanwhile the snake_case attributes are added by COMPAS IFC for simplified access to many aspects of IFC entity.
>>> window.Name
'M_Fixed:4835mm x 2420mm:4835mm x 2420mm:145788'
>>> window.ObjectType
'4835mm x 2420mm'
>>> window.OverallHeight
2.419999999999998
>>> window.OverallWidth
4.834999999999996
Spatial Hierarchy
In IFC, entities are organized in a spatial hierarchy, meaning that each entity can have a parent and children.
For example an IfcWindow is a child of a IfcBuildingStorey and usually have no children.
>>> window.parent
<#39 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 1">
>>> window.children
[]
The parent of an IfcBuildingStorey must be a IfcBuilding and can have many type of children, such as IfcSpace, IfcWall, IfcWindow, etc.
>>> building_storey = window.parent
>>> building_storey.parent
<#36 IfcBuilding "None">
>>> building_storey.children
[<#514 IfcSpace "A101">, <#4553 IfcWallStandardCase "Basic Wall:Interior - Partition (92mm Stud):139783">, <#6921 IfcWindow "M_Fixed:750mm x 2200mm:750mm x 2200mm:146885">, ...]
You can also use Entity.print_spatial_hierarchy() to print the spatial hierarchy of an entity in a tree view, with the current entity highlighted with ** signs.
>>> building_storey.print_spatial_hierarchy(max_depth=3)
================================================================================
Spatial hierarchy of <#39 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 1">
================================================================================
└── <#34 IfcProject "0001">
└── <#38274 IfcSite "Default">
└── <#36 IfcBuilding "None">
├── <#47 IfcBuildingStorey "T/FDN">
├── **<#39 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 1">**
├── <#43 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 2">
└── <#51 IfcBuildingStorey "Roof">
Geometric Representation
Entities that represents a physical product, need to be placed in a spatial context and have a geometric representation.
These two aspects are very complex when expressed in raw IFC classes, COMPAS IFC provides simplified access to these two aspects through the Entity.frame and Entity.geometry properties,
which uses COMPAS data structures that are much easier to interact with.
>>> window.frame
Frame(point=Point(x=0.0, y=0.0, z=0.0), xaxis=Vector(x=1.0, y=0.0, z=0.0), yaxis=Vector(x=0.0, y=1.0, z=0.0))
>>> window.geometry
<compas_ifc.brep.tessellatedbrep.TessellatedBrep object at 0x0000022A8BED8640>
>>> window.geometry.to_mesh()
<Mesh with 56 vertices, 108 faces, 162 edges>
For more details about the Entity.frame and Entity.geometry properties, please refer to the advanced.geometry tutorial.
Custom Properties
Most IFC entities are allowed to have custom properties or so-called Psets, they can be accessed conveniently through the Entity.properties dictionary.
>>> window.properties
{'Pset_WindowCommon': {'Reference': 'M_Fixed:4835mm x 2420mm', 'IsExternal': True, 'FireRating': 'FireRating'}, ...}
Next Steps
In the next tutorial, we will explore how to create an IFC model from scratch, including creating entities, setting up spatial hierarchy, and adding custom properties.