Hello World - Model Basics
This is a hello-world tutorial for the COMPAS IFC package. It shows how to load an IFC file and and inspect its contents.
Load an IFC model
An IFC model can be simply loaded given its file path:
>>> from compas_ifc.model import Model
>>> model = Model("data/Duplex_A_20110907.ifc")
IFC file loaded: data/Duplex_A_20110907.ifc
Loading geometries...
Time to load all 286 geometries 0.932s
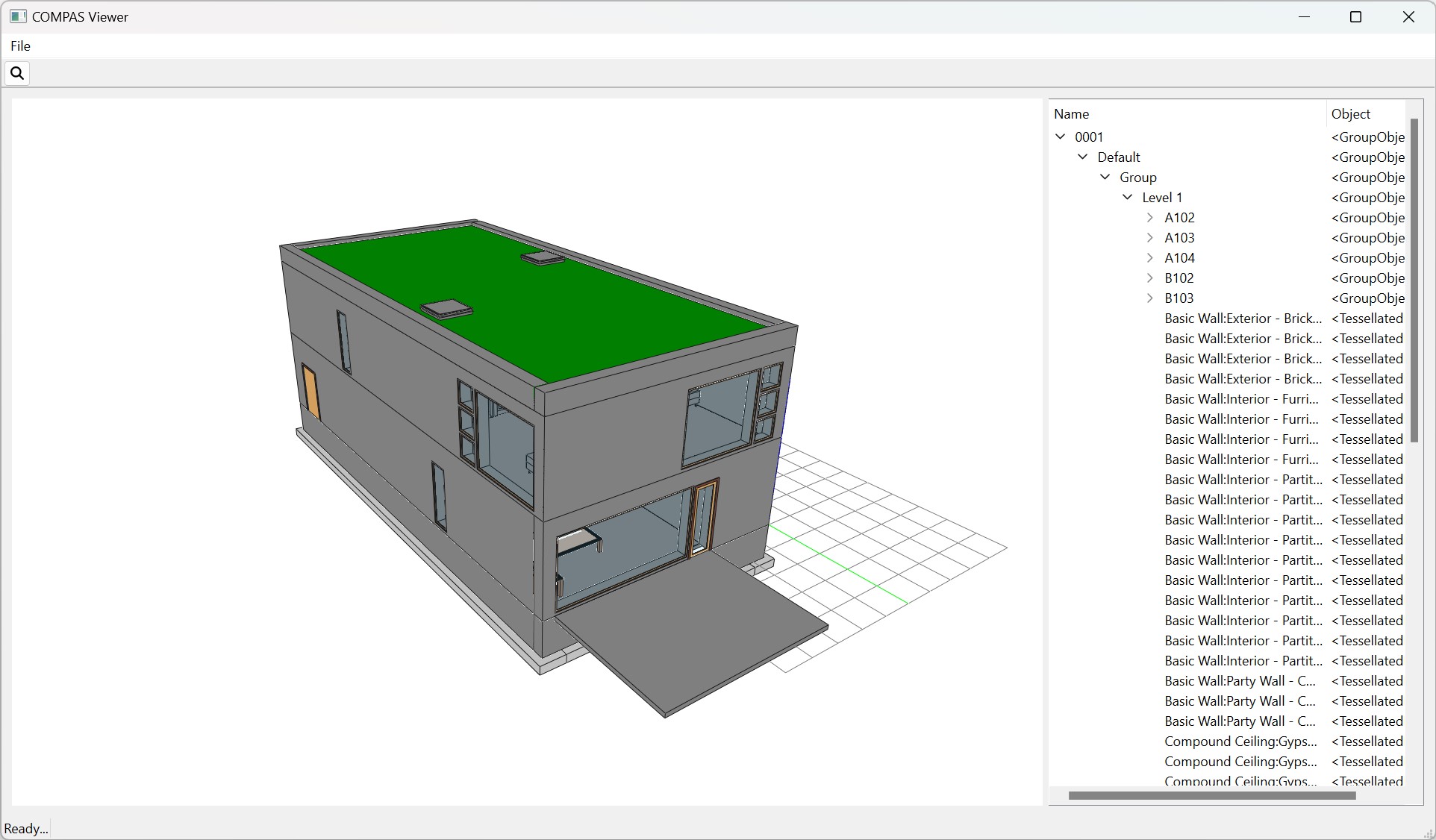
Visualize the model
With Model.show() function, the model can be visualised with the built-in viewer.
>>> model.show()
Note
compas_viewer needs to be installed to use this function.
Model functions
The Model class provides a set of APIs to interact with the IFC model. For example:
>>> model.print_summary()
================================================================================
Schema: IFC2X3
File: data/Duplex_A_20110907.ifc
Size: 2.31 MB
Project: 0001
Description: None
Number of sites: 1
Number of buildings: 1
Number of building elements: 157
================================================================================
An IFC file is essentially a collection of entities, organized in a spatial hierarchy.
Model.print_spatial_hierarchy() function will print the spatial hierarchy of the model in a tree view.
An optional max_depth parameter can be used to limit the depth of the hierarchy.
>>> model.print_spatial_hierarchy(max_depth=3)
================================================================================
Spatial hierarchy of <#34 IfcProject "0001">
================================================================================
└── <#34 IfcProject "0001">
└── <#38274 IfcSite "Default">
└── <#36 IfcBuilding "None">
├── <#43 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 2">
├── <#39 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 1">
├── <#51 IfcBuildingStorey "Roof">
└── <#47 IfcBuildingStorey "T/FDN">
Model.save() function will save the model to a new IFC file.
>>> model.save("data/Duplex_A_20110907_COPY.ifc")
IFC file saved: data/Duplex_A_20110907_COPY.ifc
Find entities
Model class provides many different ways to find specific entities, through their IFC type, entity name, IFC file ID and entity Global ID.
>>> model.get_entities_by_type("IfcRoof")
[<#22475 IfcRoof "Basic Roof:Live Roof over Wood Joist Flat Roof:184483">]
>>> model.get_entities_by_name("Basic Roof:Live Roof over Wood Joist Flat Roof:184483")
[<#22475 IfcRoof "Basic Roof:Live Roof over Wood Joist Flat Roof:184483">]
>>> model.get_entity_by_id(22475)
<#22475 IfcRoof "Basic Roof:Live Roof over Wood Joist Flat Roof:184483">
>>> model.get_entity_by_global_id("0jf0rYHfX3RAB3bSIRjmxl")
<#22475 IfcRoof "Basic Roof:Live Roof over Wood Joist Flat Roof:184483">
Shortcuts
Besides above functions, Model class also provides a set of shortcuts for quick access to the most commonly used entities.
>>> model.project
<#34 IfcProject "0001">
>>> model.sites
[<#38274 IfcSite "Default">]
>>> model.buildings
[<#36 IfcBuilding "None">]
>>> model.building_storeys
[<#39 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 1">, <#43 IfcBuildingStorey "Level 2">, <#47 IfcBuildingStorey "T/FDN">, <#51 IfcBuildingStorey "Roof">]
>>> model.building_elements
[<#4131 IfcWallStandardCase "Basic Wall:Interior - Partition (92mm Stud):138584">, <#4287 IfcWallStandardCase "Basic Wall:Party Wall - CMU Residential Unit Dimising Wall:139234">,...]
Next Steps
In the next tutorial, we will explore the Entity APIs to inspect and manipulate individual IFC entities.