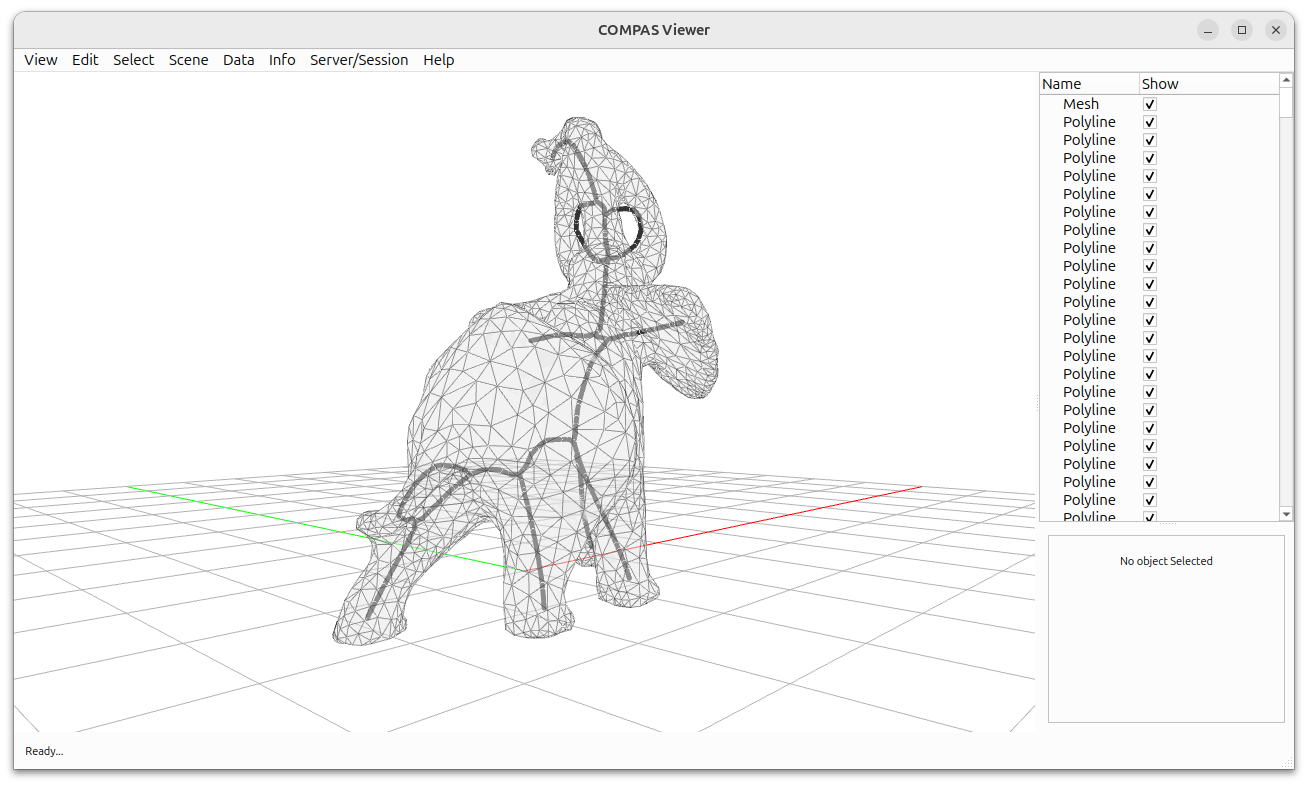
Mesh Skeletonization
This example demonstrates how to compute the geometric skeleton of a triangle mesh using COMPAS CGAL.
Key Features:
Loading and transforming OFF mesh files
Mesh subdivision using Loop scheme
Skeleton computation using mean curvature flow
Visualization of mesh and skeleton polylines
import math
from pathlib import Path
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
from compas.geometry import Polyline
from compas.geometry import Rotation
from compas.geometry import Scale
from compas.geometry import Translation
from compas_viewer import Viewer
from compas_cgal.skeletonization import mesh_skeleton
def main():
"""Skeletonize a mesh."""
input_file = Path(__file__).parent.parent.parent / "data" / "elephant.off"
rotation_x = Rotation.from_axis_and_angle([1, 0, 0], math.radians(60))
rotation_y = Rotation.from_axis_and_angle([0, 1, 0], math.radians(5))
rotation = rotation_y * rotation_x
scale = Scale.from_factors([5, 5, 5])
translation = Translation.from_vector([0, 0, 2])
mesh = Mesh.from_off(input_file).transformed(translation * rotation * scale)
# mesh = mesh.subdivided("loop")
v, f = mesh.to_vertices_and_faces(triangulated=True)
skeleton_edges = mesh_skeleton((v, f))
polylines = []
for start_point, end_point in skeleton_edges:
polyline = Polyline([start_point, end_point])
polylines.append(polyline)
return mesh, polylines
mesh, polylines = main()
# ==============================================================================
# Visualize
# ==============================================================================
viewer = Viewer()
viewer.renderer.camera.target = [0, 0, 1.5]
viewer.renderer.camera.position = [-5, -5, 1.5]
viewer.scene.add(mesh, opacity=0.5, show_points=False)
for polyline in polylines:
viewer.scene.add(polyline, linewidth=5, show_points=True)
viewer.show()