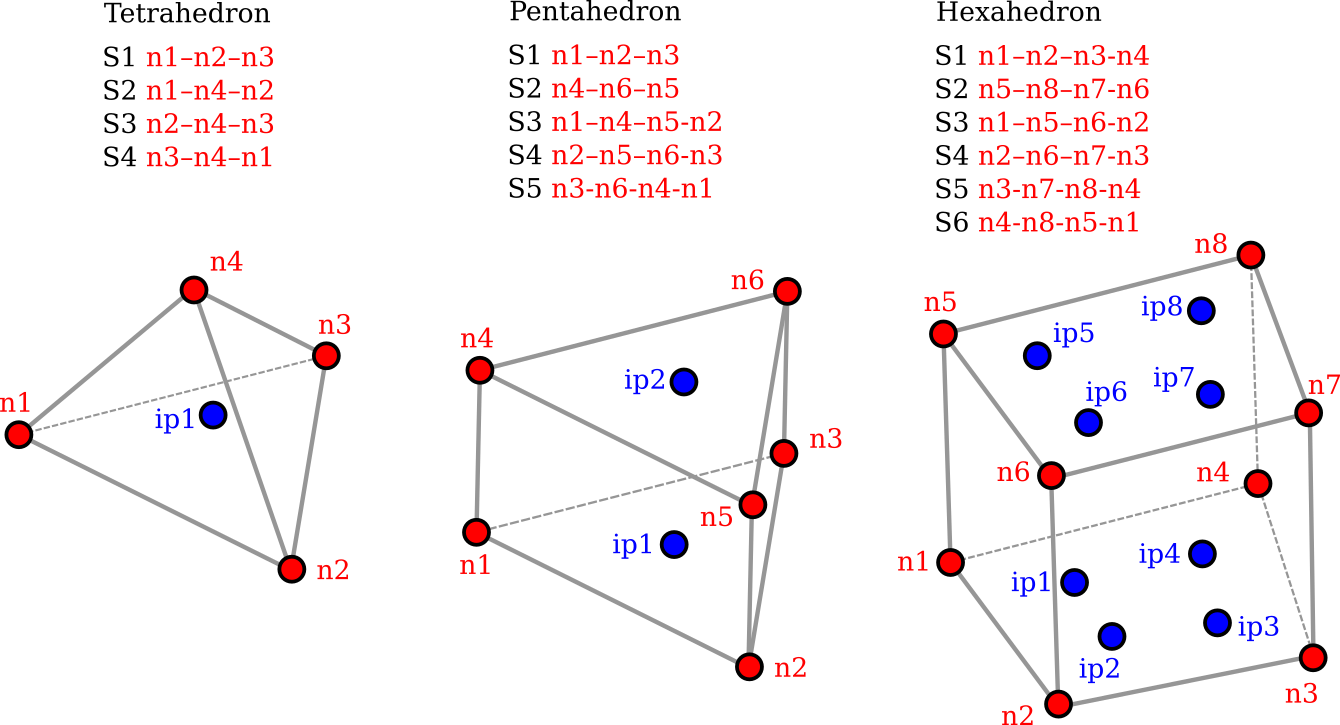
Sections
This page shows how Section objects are added to the Structure object, here given as mdl. A variety of Section objects exist for representing 1D, 2D and 3D elements.
Adding sections
Element objects that are added to the Structure do not yet have a complete description of their geometry, and so must have a Section object associated with them. Section classes are first imported from module compas_fea.structure.section and then objects instantiated and added to the .sections dictionary of the Structure object. This is done with the help of the method .add() for either a single or a list of Section objects, with name as the string key. As the section geometry will differ for each class, the input data will vary for the different types of Section objects, these inputs are summarised for each section later on this page. In the following example, the radius r is required for adding a CircularSection object and the thickness t for a ShellSection object. Note: SI units should be used, this includes the use of metres m for cross-section dimensions, not millimetres mm.
from compas_fea.structure import CircularSection
mdl.add(CircularSection(name='sec_circ', r=0.010)) # add a CircularSection with radius 10 mm
from compas_fea.structure import ShellSection
mdl.add(ShellSection(name='sec_shell', t=0.005)) # add a ShellSection with thickness 5 mm
Geometric properties
Not only will the user input geometry data be available for viewing or editing a Section object, but other geometric data will also be automatically calculated, such as the area and second moments of area. The objects are accessed through the structure.sections dictionary using the string key to access the Section object attributes.
>>> mdl.sections['sec_circ'].geometry # view or edit the object through attributes
{'r': 0.01, 'D': 0.02, 'A': 0.0003141592653, 'Ixx': 7.853981633e-09, 'Iyy': 7.853981633e-09, 'Ixy': 0}
>>> mdl.sections['sec_circ'].__name__
'CircularSection'
>>> print(mdl.sections['sec_circ']) # print a summary of section `sec_circ`
compas_fea CircularSection object
---------------------------------
name : sec_circ
r : 0.01
D : 0.02
A : 0.0003141592653589793
Ixx : 7.853981633974483e-09
Iyy : 7.853981633974483e-09
Ixy : 0
J : 1.5707963267948965e-08
Types
There are a variety of 1D: AngleSection, SpringSection, BoxSection, CircularSection, GeneralSection, ISection, PipeSection, RectangularSection, TrapezoidalSection, TrussSection, 2D: ShellSection, MembraneSection and 3D: SolidSection objects that can be imported, and then added as objects with the .add() method.
Truss
A TrussSection can take only axial forces (no shear forces or bending and torsion moments), and so only requires the cross-section area A.
from compas_fea.structure import TrussSection
mdl.add(TrussSection(name='sec_truss', A=0.0050))
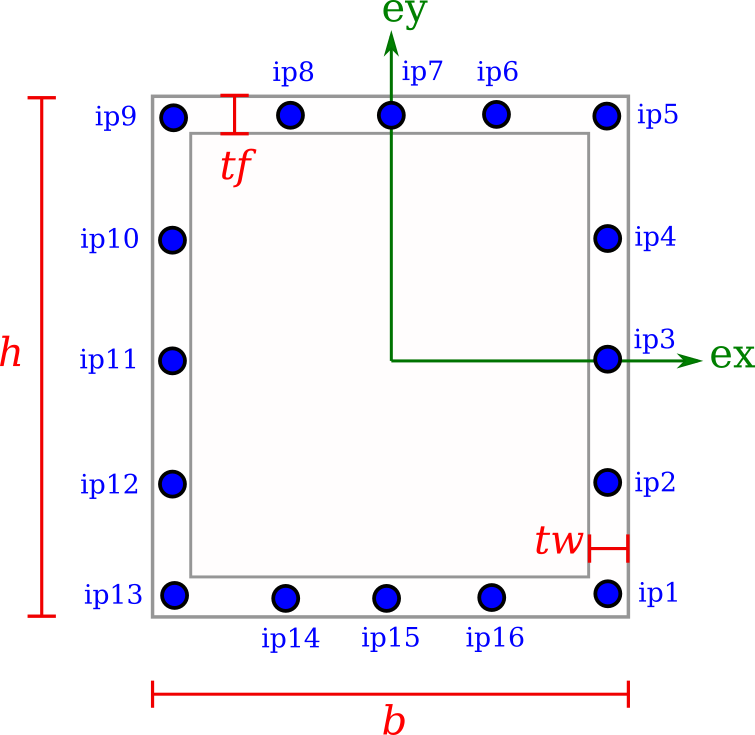
Box
A hollow BoxSection requires the width b, height h, thickness of web tw and thickness of flange tf.
from compas_fea.structure import BoxSection
mdl.add(BoxSection(name='sec_box', b=0.1, h=0.2, tw=0.003, tf=0.005))
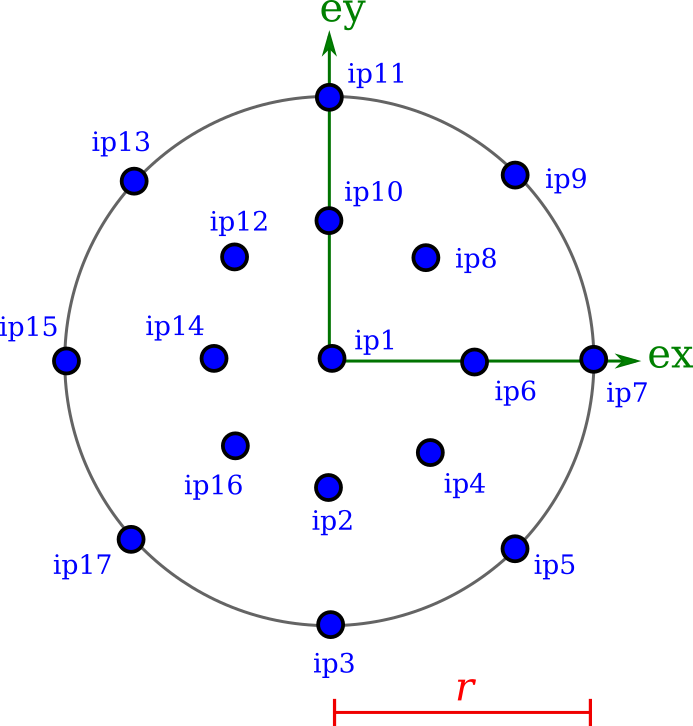
Circular
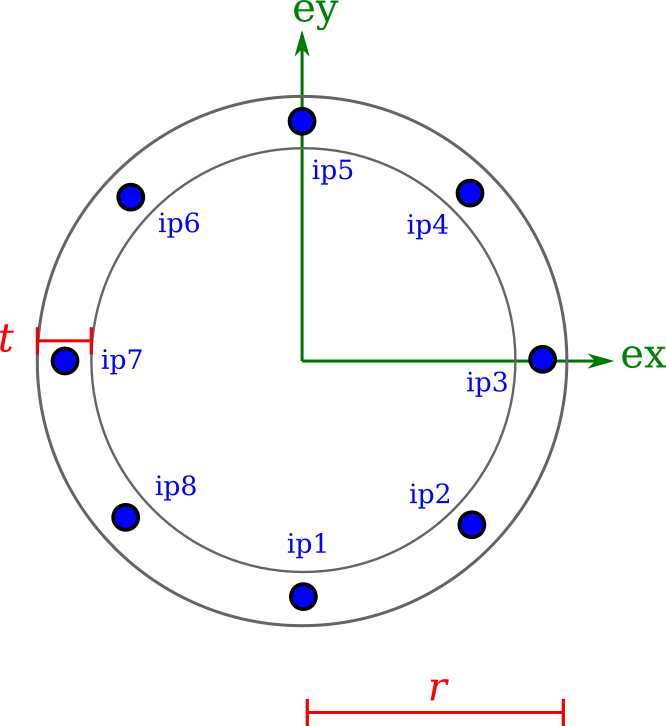
A solid CircularSection requires the radius r.
from compas_fea.structure import CircularSection
mdl.add(CircularSection(name='sec_circular', r=0.01))
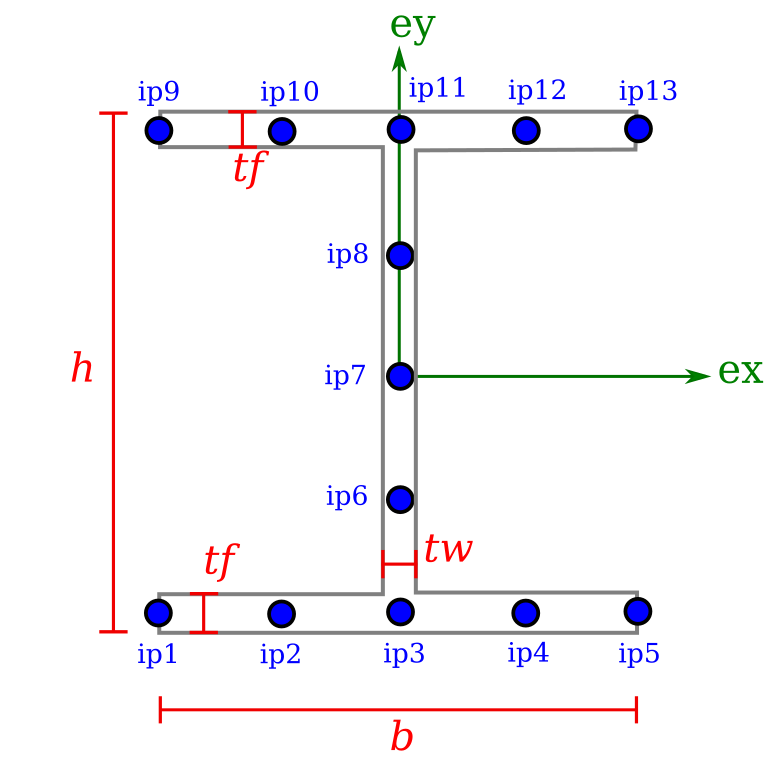
I
An ISection requires the width b, height h, thickness of web tw and thickness of flange tf.
from compas_fea.structure import ISection
mdl.add(ISection(name='sec_I', b=0.1, h=0.2, tw=0.003, tf=0.005))
Angle
An unequal AngleSection requires the width b, height h and thickness t.
from compas_fea.structure import AngleSection
mdl.add(AngleSection(name='sec_angle', b=0.1, h=0.2, t=0.003))
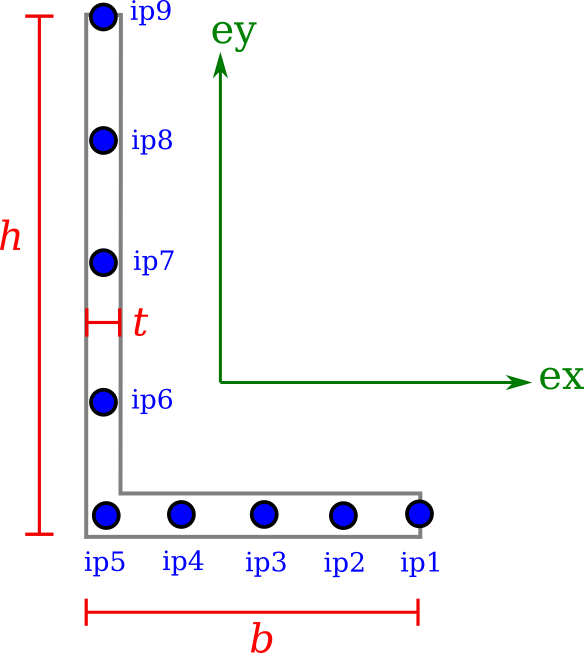
Pipe
A hollow PipeSection requires the radius r and thickness t.
from compas_fea.structure import PipeSection
mdl.add(PipeSection(name='sec_pipe', r=0.1, t=0.005))
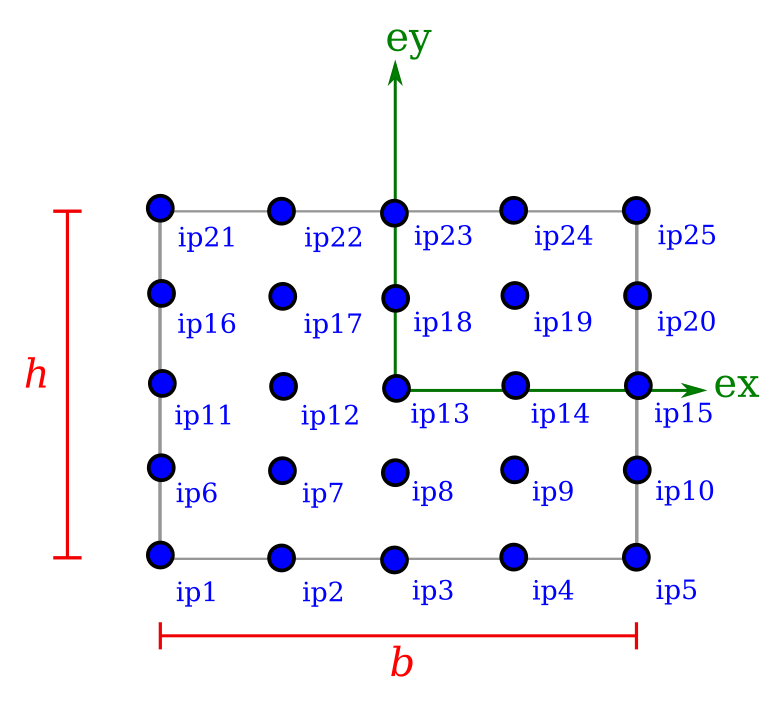
Rectangular
A solid RectangularSection requires the width b and height h.
from compas_fea.structure import RectangularSection
mdl.add(RectangularSection(name='sec_rectangular', b=0.1, h=0.2))
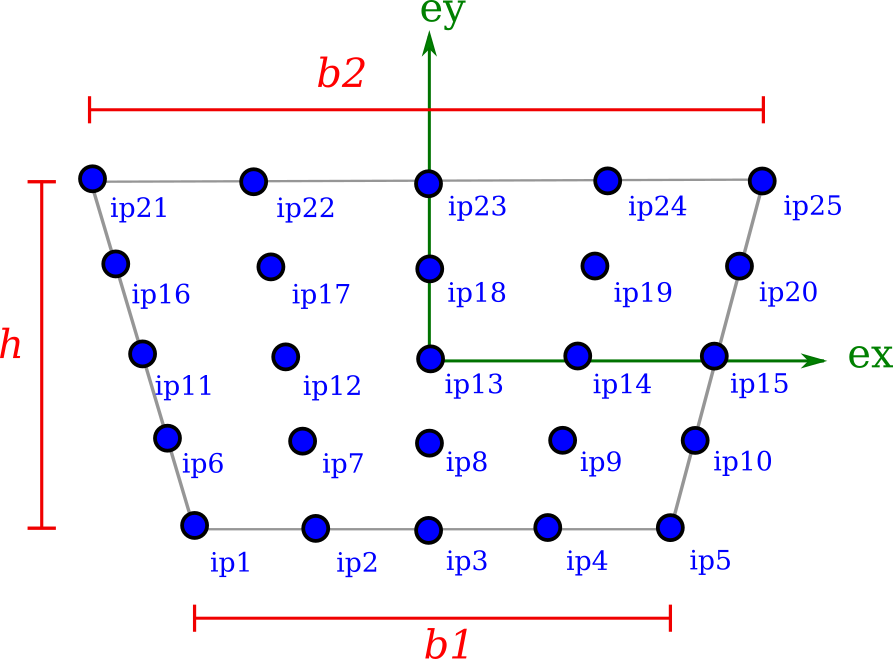
Trapezoidal
A TrapezoidalSection requires the base width b1, top width b2 and height h.
from compas_fea.structure import TrapezoidalSection
mdl.add(TrapezoidalSection(name='sec_trapezoidal', b1=0.1, b2=0.05, h=0.2))
General
A GeneralSection takes explicit cross-section information: area A, second moment of area about axis (ex) Ixx, cross moment of area Ixy, second moment of area about axis (ey) Iyy, torsional rigidity J, sectorial moment g0, warping constant gw.
Shell
The area of a shell or membrane element is known from the geometry of the element through the co-ordinates of the nodes it connects to. All that is needed for the definition of a ShellSection is the thickness t. For a MembraneElement, the dimensions will be used to calculate the element cross-section area for membrane forces, while a ShellElement will also use the geometry for shear forces, bending moments and torsional moments.
from compas_fea.structure import ShellSection
mdl.add(ShellSection(name='sec_shell', t=0.005))
from compas_fea.structure import MembraneSection
mdl.add(MembraneSection(name='sec_membrane', t=0.005))
Solid
The volume of a solid element is known from the geometry of the element through the co-ordinates of the nodes it connects to. The creation of a SolidSection therefore only needs the name of the object.
from compas_fea.structure import SolidSection
mdl.add(SolidSection(name='sec_solid'))